Experiments were previously called Splits.
| Audience | Marketers and analysts who want to compare the effectiveness of different campaign strategies using real audience data. |
| Prerequisites |
Run controlled experiments directly in Customer Studio by creating randomized groups to test and measure the true impact of your marketing campaigns.
Learning Objectives
After reading this article, you will be able to:
- Understand when and why to use audience experiments
- Create A/B or multivariate experiment groups within a saved audience
- Sync each group to separate treatments, campaigns, or destinations
- Measure campaign effectiveness using Experiments in Campaign Intelligence
- Use stratified sampling to ensure balanced test and control groups
- Access holdout group logs for detailed post-campaign reporting in your warehouse
Overview
Audience Experiments enable you to create randomized audience groups for accurate, controlled testing of campaign strategies. By assigning audience members to distinct test groups, you can compare outcomes between treatments, channels, or creatives and understand what’s truly driving performance.
You can also configure experiments directly on A/B split nodes within Journeys.
What you can measure
- Incrementality: Did your campaign actually cause the desired outcome?
- A/B/n testing: Compare creatives, messages, or channels.
- Personalization impact: Determine whether tailored experiences outperform generic ones.
- Channel effectiveness: Identify which channels drive more downstream conversions.
When to use experiments
Use audience experiments when you want to move beyond assumptions like:
- Correlation: “Purchases increased—but was it because of the campaign?”
- Attribution: “A user converted after seeing my ad—but would they have converted anyway?”
Running a controlled experiment isolates the impact of your campaign by comparing outcomes between randomized groups.
How audience experiments work
| Stage | What it means | Hightouch feature |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Define your audience | Choose your target group | Build audiences |
| 2. Create experiment groups | Randomly assign audience members | Experiments |
| 3. Apply a treatment | Run a campaign for one or more groups | Syncs |
| 4. Measure results | Compare outcomes between groups | Experiments |
| 5. Interpret the impact | Evaluate lift and statistical significance | Experiment results chart |
Example use cases
Email campaign holdout
- 50/50 experiment
- Group A receives promotional email
- Group B is held out
- Compare conversions or revenue per user
Ad creative A/B test
- Groups A and B synced to separate ad sets
- Compare CTR, CPC, or downstream conversion
Personalization test
- Group A receives personalized product recommendations
- Group B receives a generic message
- Compare engagement and purchases
Onboarding lifecycle experiment
- Test different onboarding flows
- Measure feature adoption or retention after 14 days
Channel comparison
- Group A receives email
- Group B receives paid ads
- Compare downstream LTV or sign-up quality
Setup steps
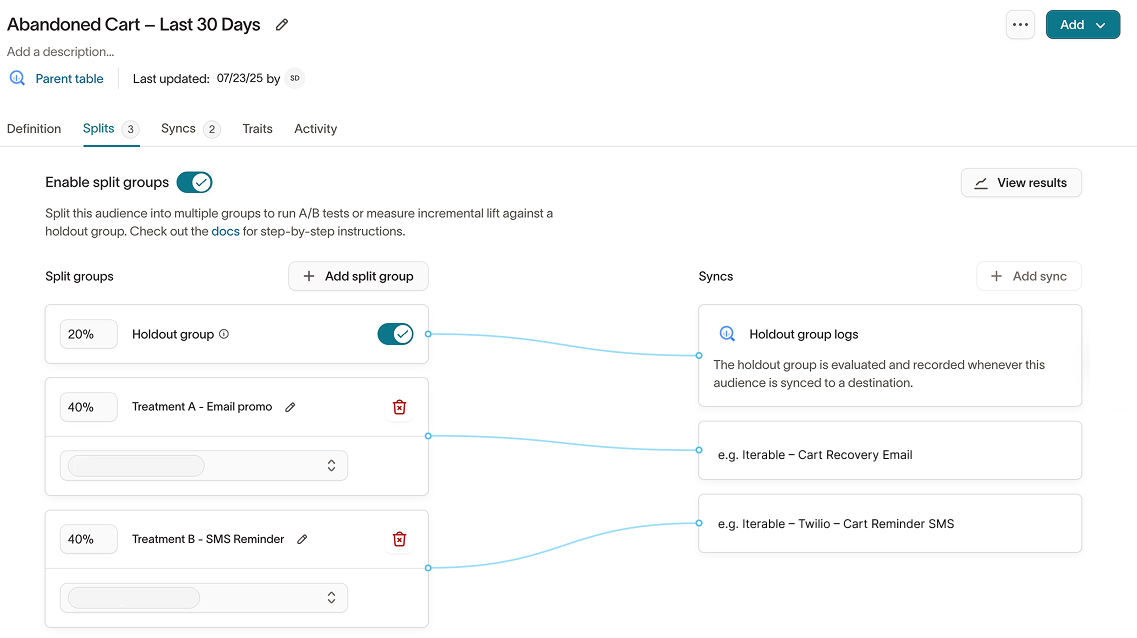
1. Create experiment groups
- Open your audience in Customer Studio.
- Navigate to the
Experimentstab. - Toggle
Enable experiment groups. - Under
Experiment groups, configure:- Number of groups (e.g., 2 for A/B tests, 3+ for multivariate)
- Percentage distribution (e.g., 50/50)
- Group names (e.g.,
Holdout,Treatment A)
- Optionally add more groups for A/B/n testing.
- For each group, configure syncs to destinations.
- Click
View resultsto begin analysis.
2. Measure results
Once your audience has at least one sync involving experiment groups, Hightouch automatically generates a corresponding Experiment.
Clicking View results opens the Experiment overview.
You can also access Experiments anytime under:
Intelligence → Experiments`
Use Experiments to:
- Compare lift across groups
- View statistical significance
- Analyze results using primary or secondary metrics
- Normalize results per member or against a baseline
Older Splits measurement charts have been deprecated. All measurement now occurs in Experiments.
Learn how to configure and interpret Experiments →
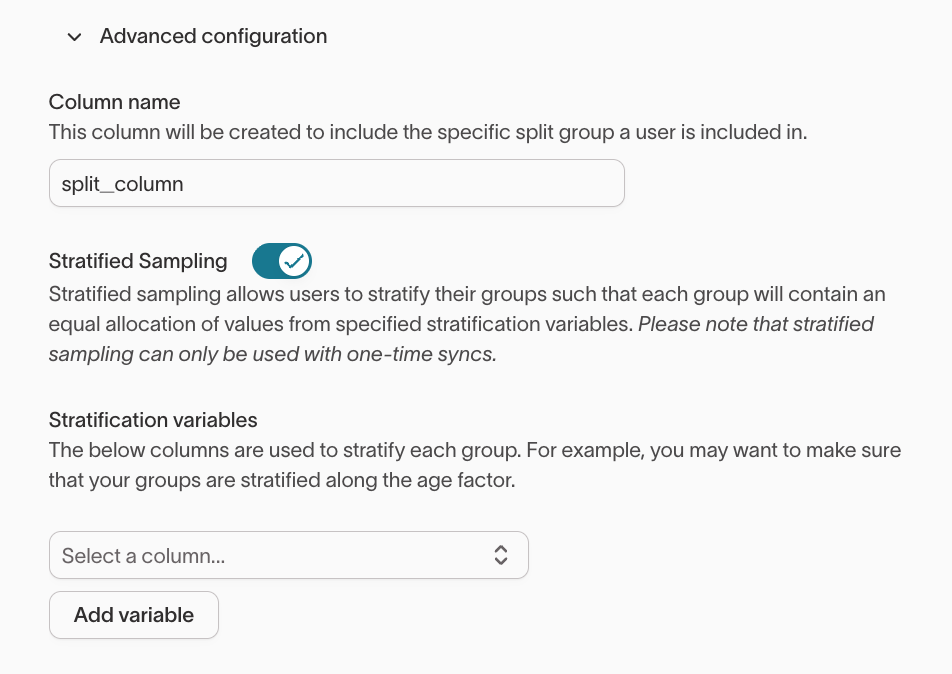
Stratified Sampling
Simple randomization may not provide balanced groups when your audience contains diverse characteristics (e.g., geography, loyalty tier). Stratified sampling ensures proportional representation across experiment groups based on selected variables.
Stratified sampling is only available for one-time syncs.
How to enable stratified sampling
- Open your audience and go to the
Experimentstab. - Under
Advanced configuration, toggleStratified sampling. - Select one or more columns to stratify by (e.g.,
loyalty_tier). - Save your changes.
Holdout group logs
Holdout group logs are used primarily by data teams to perform row-level warehouse analysis. Marketers should rely on Experiment results in the Customer Studio UI.
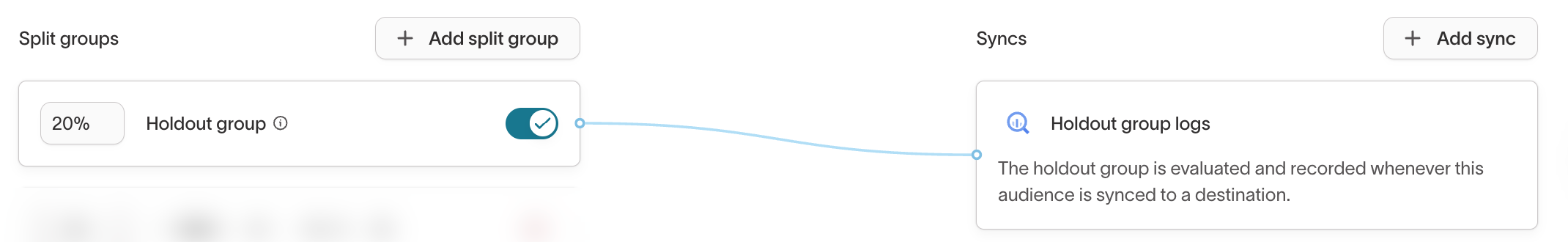
Holdout group logs track which rows were excluded from a sync as part of a holdout (e.g., a 20% control group). This enables advanced SQL or BI analysis.
How to enable holdout group logs
- to enable the Holdout group logs feature flag. Requirements:
- Lightning sync engine
- A destination with write access to your warehouse
- In your workspace:
- Go to
Integrations → Sources - Select a source and open the
Sync Logstab - Enable
Audience holdout group logs
- Go to
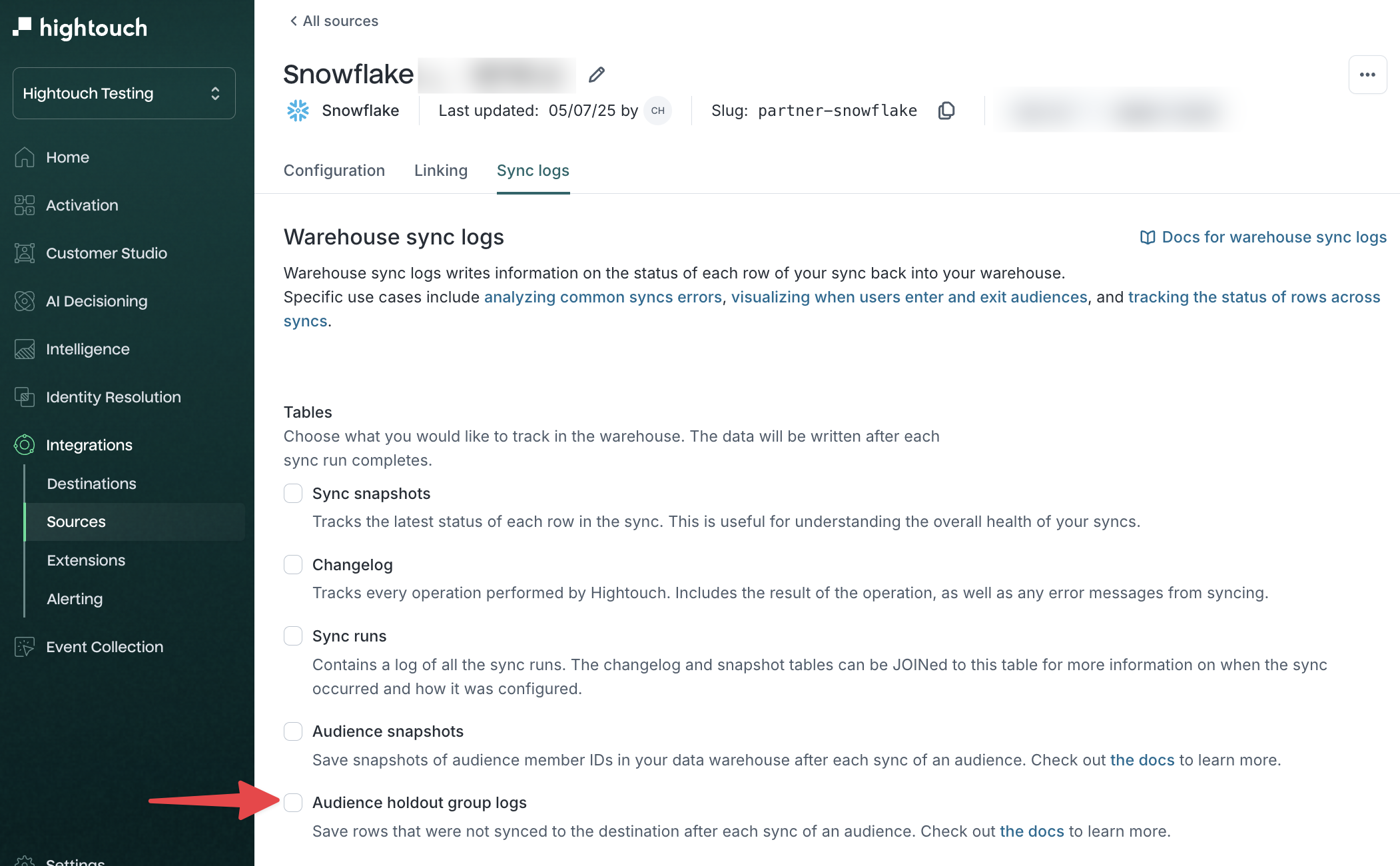
When enabled, Hightouch logs excluded rows in the hightouch_audit.audience_holdout table.
Table definition
| COLUMN | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
sync_id | Sync ID |
sync_run_id | Sync run ID |
model_id | Model/audience ID |
timestamp | Timestamp of sync |
row_id | Primary key value from the model |
fields | JSON snapshot of model data |
split_group | Name of the experiment group |